
Rotation positioning accuracy is one of the key indicators in modern manufacturing industry, which is crucial for product quality and process stability. With the continuous development of manufacturing technology and standards, the requirements for rotation positioning accuracy are becoming increasingly stringent. This article explores the definition of rotation positioning accuracy according to ISO 230, analyzes the application of rotation positioning technology in different industries, and discusses its future development trends.
What are the units of rotation positioning accuracy?
Positioning accuracy can be expressed in terms of distance or angle, and the units of specification vary depending on different applications and industry standards. Here are the common units and specifications for positioning accuracy:
Distance Units
Positioning accuracy in terms of distance is typically expressed in millimeters (mm) or micrometers (μm). According to ISO 230 standards, distance specifications may include absolute accuracy, relative accuracy, repeatability accuracy, etc., and have specific measurement methods and tolerance ranges.
Angle Units
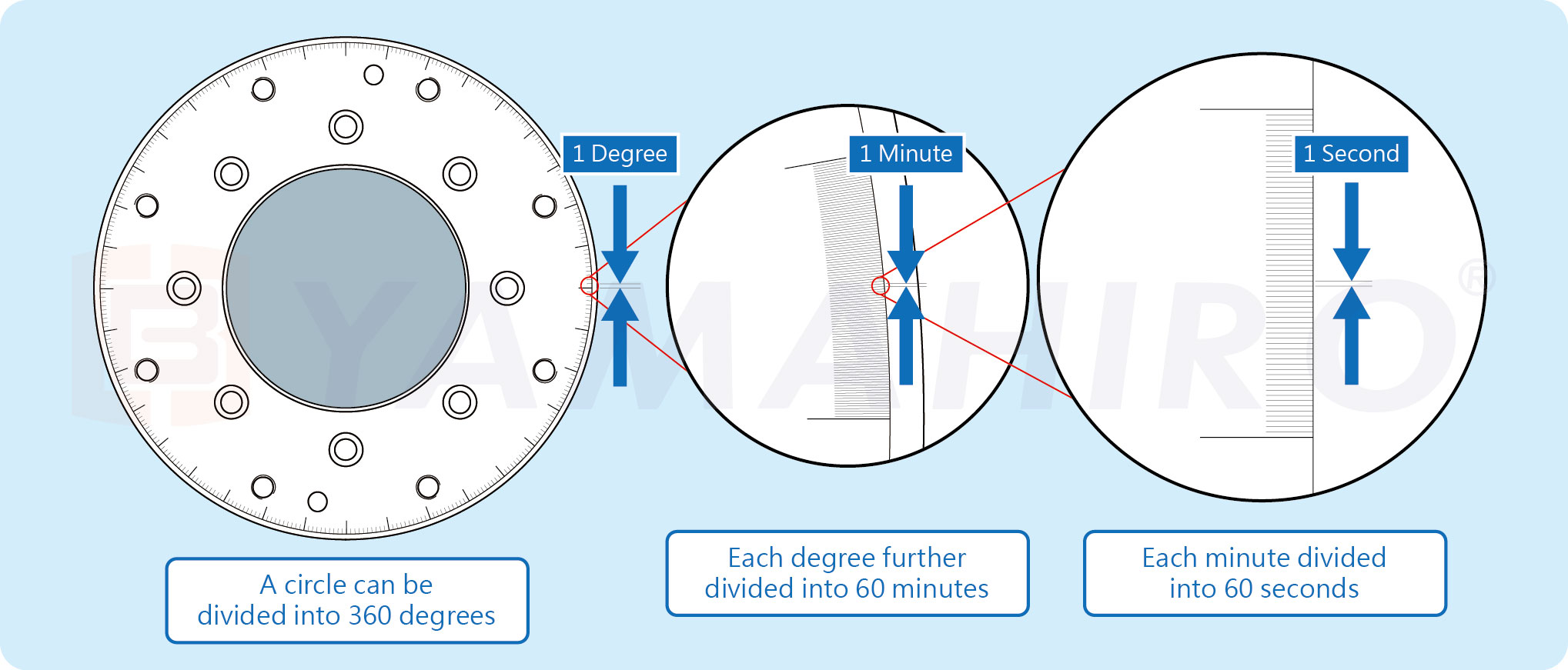
▲ Angle unit illustration
When measuring and specifying positioning accuracy, various factors need to be considered, such as the accuracy of measurement equipment, measurement environment, material characteristics of workpieces, etc. Therefore, the unit specifications for positioning accuracy need to be determined according to specific applications and standards to ensure the accuracy of measurement results.
Rotation positioning accuracy is crucial for the manufacturing process and product quality. In the manufacturing process, precise rotation positioning ensures that machining centers can accurately position and process workpieces, thereby ensuring that the dimensions and shapes of products meet design requirements. Accurate rotation positioning can reduce errors and rework in the machining process, improve production efficiency, and yield rate.
In terms of product quality, rotation positioning accuracy directly affects the precision and surface quality of products. If the rotation positioning is inaccurate, it will result in workpiece positioning deviation, leading to problems such as inaccurate dimensions, rough surfaces, and irregular shapes, thereby affecting the functional and appearance quality of products.
Moreover, rotation positioning accuracy plays a key role in the manufacturing process. It ensures the alignment accuracy between different processing steps, achieving consistency and coherence in multi-step processing. At the same time, precise rotation positioning can reduce material waste and production costs in the manufacturing process, improve production efficiency, and control the quality level.
In summary, rotation positioning accuracy has a significant impact on the manufacturing process and product quality, not only related to the precision and surface quality of products but also directly affecting production efficiency and cost control. Therefore, it is essential to emphasize the improvement and control of rotation positioning accuracy in the manufacturing industry.
---HERBAO---


